Asthma
Constant wheezing and breathlessness?
Learn More
Dr. Manoj K Goel is the Principal Director and Head, Department of Pulmonology, Critical Care, and Sleep Medicine at Fortis Memorial Research Institute, Gurugram. He holds an MBBS and MD from King George’s Medical College, Lucknow. He has received advanced training in Interventional Pulmonology at the University of Lille, France; Critical Care at Erasme University Hospital, Brussels, Belgium; Sleep Medicine at Prince Royal Alfred Hospital, Sydney; and EBUS Bronchoscopy at Royal Brisbane and Women’s Hospital, Australia.
Dr. Goel specializes in treating critically ill patients with acute and chronic respiratory failure and multisystem disorders affecting the lungs. He is proficient in advanced bronchoscopic procedures and pulmonary interventions such as EBUS, Radial EBUS-guided lung biopsy, Cryotechnique, Electrosurgical removal of bronchial tumors, and airway stenting.
Member, Expert Committee:
Educational Ventures:
Oration Awards:
Research and Publications:
Healthcare Achievement Awards:
In asthma treatment, inhalers are one of the most effective ways to deliver medicine directly to the lungs. Here, I am demonstrating the Metered Dose Inhaler (MDI), and I want to begin by helping you understand its basic parts. The mouthpiece is where you inhale the medicine, the protective cap keeps it clean, and the actuator is the part you press to release a fixed dose of medication.
Along with the inhaler, I also recommend using a spacer because it helps improve the delivery of the medicine. The spacer reduces the need to coordinate pressing the inhaler and breathing in at the same time, and ensures that more medicine reaches your lungs instead of getting deposited in your mouth or throat. I will show how to insert the MDI into the spacer so it is ready for use.
Once the inhaler and spacer are assembled, the correct technique is important. First, shake the inhaler well. Insert it into the spacer, press once to release a puff into the chamber, and then inhale slowly and deeply through your mouth. After inhaling, hold your breath for about 10 seconds so the medicine can settle properly in your airways and provide better asthma control.
For many individuals with asthma, inhalers play an important role in day-to-day symptom control. Here I am showing how to use a Metered Dose Inhaler (MDI) in a simple and effective manner. Before starting, make sure you recognize the essential parts of your device—the mouthpiece, the cap, and the portion that delivers the medication when pressed.
To get an accurate dose, begin by shaking the inhaler thoroughly. This prepares the medicine and ensures it is ready for use. Once done, open the cap and breathe out comfortably so your lungs are prepared to take in the medication.
Next, place the inhaler in your mouth, press it once, and draw a slow, steady breath inwards. After taking the puff, pause for a moment by holding your breath for a few seconds. This gives the medicine enough time to reach deeper parts of your lungs.
After completing the dose, rinse your mouth with plain water. This helps remove any leftover particles and keeps your mouth clean and irritation-free.
In this demonstration, I am showing you how to use a Revolizer device to inhale Rotacaps. Before using it, it is important to understand its components. The Revolizer has a mouthpiece, a chamber where the capsule is placed, and a base that helps you take a smooth and controlled breath. Rotacaps themselves have two sections—a colored cap and a transparent body.
To begin, open the Revolizer and separate the Rotacap into its two parts. Insert the transparent half of the capsule into the chamber and close the device firmly. You will hear a clicking sound, which indicates that the capsule has been punctured and is ready for inhalation.
Now breathe out gently to empty your lungs. Then place the mouthpiece between your lips and inhale deeply and steadily. After taking a full breath in, hold it for around 10 seconds so the powdered medicine has enough time to settle in your airways.
Open the Revolizer and check if the capsule is empty. If any powder remains, repeat the inhalation once more to ensure the complete dose is taken. After finishing, rinse your mouth with clean water to remove any residual medication.
In this video, I explain how to use the Rotahaler step by step. I first show all the parts of the device—the mouthpiece, the rotary chamber, and the soft intake area where the transparent portion of the rotacap is placed.
I begin by opening the Rotahaler and separating the coloured and transparent parts of the rotacap. The transparent half is placed into the soft intake area. After closing the device, I twist the rotary chamber until a click is heard, which indicates that the capsule has opened and is ready for inhalation.
Then I breathe out fully to empty the lungs, take a long and steady breath through the device, hold it for about 10 seconds, and breathe out normally. I also check whether the capsule is empty; if not, I repeat one more breath in the same way. At the end, I remind patients to rinse their mouth with plain water so that any remaining medicine is washed away.
In this video, I demonstrate the correct way to use the Symbicort inhaler. I begin by showing its main components—the white mouthpiece, the base of the inhaler, and the dose counter on top, which helps track how many doses are left.
Before using it, I shake the inhaler well so the medicine inside gets evenly mixed. Then I breathe out fully to empty the lungs, place the mouthpiece between the lips, and take a deep, steady breath in while pressing the inhaler once to release the medication.
After inhaling, I hold my breath for about 10 seconds to let the medicine settle properly in the airways, and then breathe out slowly. I also remind viewers to rinse their mouth with plain water after using Symbicort to remove any leftover medicine.
In this video, I explain how to use the Lupihaler correctly. I begin by showing all its parts—the lid, the mouthpiece, the base, the capsule slot, and the two side buttons that help break the capsule.
I take a rotacap, open it, and place the transparent portion into the capsule slot. Then I close the mouthpiece firmly over the base to lock the device. I also explain the importance of keeping the Lupihaler straight and upright, without tilting it in any direction, to ensure proper functioning.
After that, I press the two buttons three to four times so the capsule breaks and the powder is released. Once the buttons are released, the capsule moves freely inside, indicating that the medicine is ready for inhalation.
I breathe out completely to empty the lungs, place the mouthpiece in my mouth, and take a deep, steady breath in. After inhaling, I hold my breath for around 10 seconds and then breathe out normally. Just like with other inhalation devices, I recommend rinsing the mouth with plain water afterward to clear any leftover medicine.
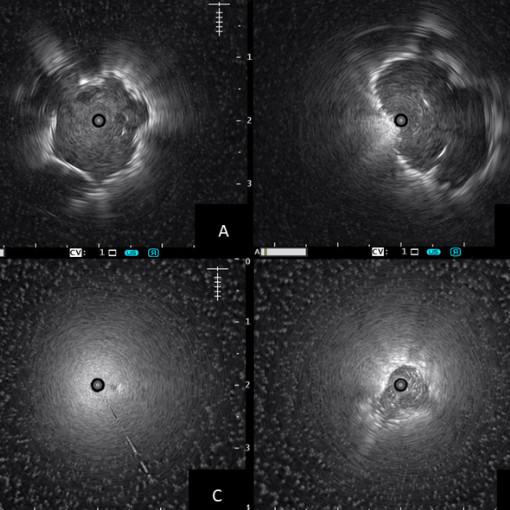
The use of Radial Probe Endobronchial Ultrasound (EBUS) is pivotal in visualizing and facilitating biopsy of peripheral pulmonary lesions with precision and minimal invasiveness. A bronchoscope is carefully guided into the distal-most airway near the lesion. The radial probe, inserted through the bronchoscope via a guide-sheath, rotates 360° to provide a circumferential scan of the lung, aiding in the accurate localization of the peripheral lesion.
Once the lesion is localized, the probe is withdrawn and appropriate biopsy tools are inserted to collect tissue samples. This precise approach enhances diagnostic yield while minimizing complications.
The accompanying video demonstrates a REBUS-guided cryobiopsy of a 14 mm peripheral nodule in the RB2aiβ sub-subsegment of the right upper lobe — showcasing advanced pulmonary intervention in real-time.

The need for bronchoscopy procedures in diagnosing and managing life-threatening pulmonary conditions in the ICU has been increasingly recognized. This handbook, "Bronchoscopy in ICU: A Practical Guide", edited by Dr. Manoj K Goel, Director Pulmonology at Fortis Memorial Research Institute, was launched during the 20th NAPCON in Ahmedabad, hosted by the National College of Chest Physicians and Indian Chest Society.
This comprehensive guide is an indispensable quick reference for pulmonologists, anesthesiologists, and critical care physicians. It also serves as an introductory resource for students, nurses, and paramedics, emphasizing safety, procedure success, and team coordination.
Covering anatomy, indications, techniques, equipment care, and complication management with abundant illustrations and expert tips, this book enhances the diagnostic and therapeutic utility of bronchoscopy in ICU settings.
As one of the top Pulmonologists and Critical Care Specialists in Delhi, Dr. Manoj Kumar Goel provides thorough and individualized care for all your respiratory and sleep health needs.
Dr. Manoj Kumar Goel utilizes the latest diagnostic tools and treatment options to ensure the best outcomes for patients.